Health & Hygiene
Cleanliness is next to Godliness
- John Wesley
Health refers to fitness of a person including physical wellbeing; hygiene refers to good practices or habits that helps to maintain one’s health. World Health Organization (WHO) defines Health as “a state of complete physical, social and mental well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity”.
Healthy people are more efficient, productive and live longer than others, good health is important. Even minor aches and pain, increases the stress level and reduces our happiness. In order to maintain a good health, one must eat well-balanced diet, drink minimum of two liters water a day, exercise regularly, keep themselves and their surroundings clean.
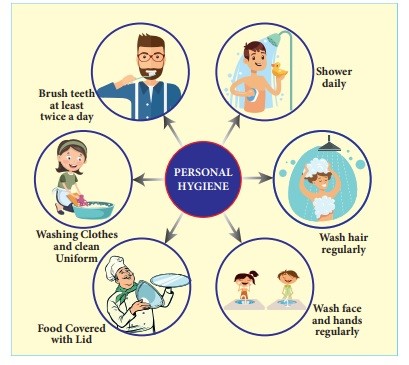
Good hygiene is important in preventing the spreading of infectious disease and helps the children and adult to lead a long and healthy life. Personal, Environment, domestic and food are the four types of Hygiene. Some of the habits to maintain good hygiene are taking bath daily, washing hands with soap after using the toilet, brushing teeth twice a day and eating well cleaned and cooked food & also avoid junk foods
WHO states that factors that affect health are: the social and economic environment, the physical environment, and the person’s individual characteristics, habits and behaviour. Each and every culture has their hygiene practices. Yet the COVID pandemic had thrown light on the importance of hygiene in our day-to-day life. It made us to learn that improper hygiene may become a threat to human life. Keeping our surrounding or environment clean is most important life that of keeping oneself clean.
“Good health and well-being” is the 3rd goal of Sustainable Development (SDG), 2015. It is the responsibility of the everyone to achieve SDG in the country. Health care centres are to be made affordable and accessible for all. In India, the state and the Union government provides medical help at free of cost and provides insurance for certain treatment when necessary.
Water plays a major role in health and hygiene. Therefore, it is important to use safe and clean water. Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH) is used widely in developing countries by non-government organisations and aid agencies. Drinking unsafe water damages health through illnesses like diarrhoea. Polluted water is the reason for many water-borne diseases which may become fatal at times. WHO states that “Worldwide, 2.2 billion people still lack access to safe drinking water. More than half of the global population does not have access to safe sanitation. Three billion people do not have access to handwashing facilities with soap. And still, 673 million people practice open defecation.”
Proper sanitation facility is very important as it impacts mainly the children and women. People living in poor sanitation facility are prone to many illnesses and diseases. “Total Sanitation Campaign” launched by Rajiv Gandhi National Drinking Water Mission in 1999, now renamed as Nirmal Bharat Abhiyan, ensured to eradicate the practice of open defecation. The key intervention areas have been identified as Individual Household Latrines (IHHL), School Sanitation & Hygiene Education, Community Sanitary Complex and Anganwadi Toilets. A nominal subsidy in the form of incentive is given to the rural poor households for construction of toilets.
The state/UT’s as well as the Union government strives to maintain health and hygiene of the people through various measures. Ministry of Health and Family welfare’s flagship program National Health Mission (NHM), with its two sub-missions, to support state and Union Territory to strengthen their health care systems so as to provide universal access to equitable, affordable and quality health care services, National Rural Health Mission (NRHM) and National Urban Health Mission (NUHM). The schemes launched by NHM are at free of cost.
Reproductive, Maternal, Neonatal, Child and Adolescent health, National Nutritional Programmes, Communicable diseases, non-communicable diseases are some of the branches in which the government launches program and schemes under National Health Mission. As a preventive measure, Mobile Medical Units (MMU’s) and Telemedicine are also being implemented by Government of Tamil Nadu with NHM to improve healthcare access in rural areas.