Cyber Security Awareness

American business magnet and Philanthropist Warren Buffett describes cyber-crime as the “number one Problem with mankind and it poses real risks to humanity”.
Cyber security is a discipline that protects critical systems/devices, personal information, networks, software, hardware and data from cyber / digital attack or hacking. It is nothing but how an individual or an organisation reduce the risk of cyber-attack.
It is also called electronic information security or information technology security. Usually, cyber-attacks are aimed at accessing, changing or destroying the personal and sensitive information of a user, extorting money from them through unknown sources. It is a deliberate attempt to exploit the confidentiality of a target organisation by external hackers.
Different ways of cyber-attacks are happening today. Some important methods of the hackers / attackers’ approaches are: Malware, Ransomware, phishing, man-in-the middle (MITM) attack, SQL Injection (SQLI), Denial of service, remote code execution and so on. There is another term in cyber security called security breech. This is not the same as cyber-attack. Instead, it is a successful event or incident in which cyber attack ends in compromise. Cyber-attack is now an international concern. Hence, it is important to have excellent cybersecurity strategies to protect sensitive information data of every individual and organisation.
The ultimate aim of cyber security is data protection. The principle of Cyber security is the CIA triad – Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability. There are 5 types of cyber security namely, Application security, Network security, Cloud security, Critical Infrastructure security and Internet of things security. Cyber security helps in securing data of various organisations. Often, the attackers target small and large companies and obtain their data. They not only attack organisation or companies, but also individuals. Hence Cyber security is must for individuals, businesses and government to protect their data.
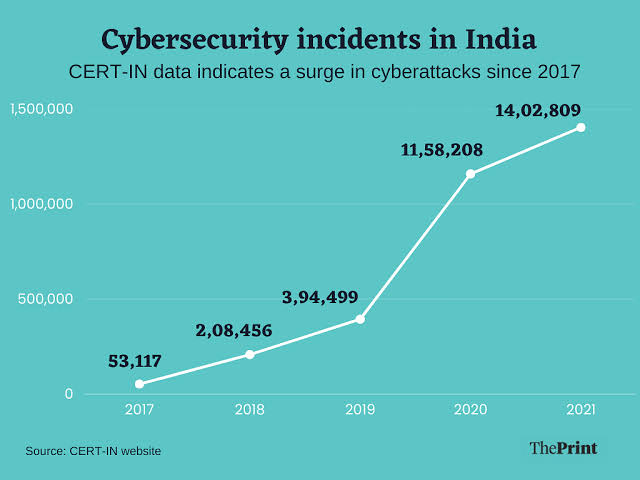
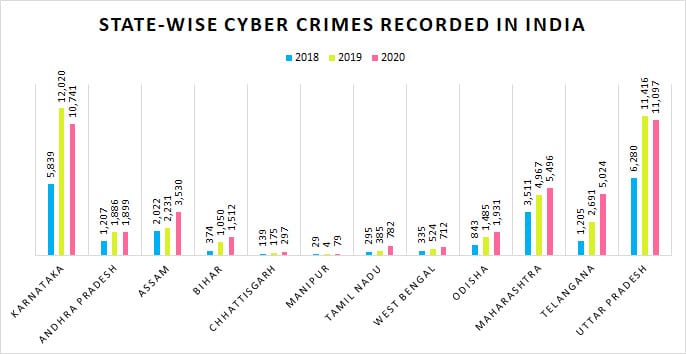
IT Act 2000, by government of India, deals with cybercrime and electronic commerce. This Act prescribes penalties for various cybercrimes and fraud through digital/economic format. In addition to this, Indian Penal Code (IPC) 1860 also covers cybercrime issues. The citizens are asked not to share sensitive information like account details, OTP, pin number and do not open any link sent by unknown person etc., to avoid fraudulent activities. Since e-commerce has become more prevalent and we are in the phase of digitalisation, it is important for every citizen to be aware of cyber-crime and cyber security. It is said that India was a top target for Cyber-attack in the year 2022. Below given are the statistic of cyber-crime happened in India (as per CERT-IN) in general and its states in particular.
Ministry of Electronics and Information system (MeitY), under the Government of India, initiated Cyber Surakshit Bharat to create a robust cybersecurity Ecosystem in India lined up with the government’s vision of ‘Digital India’. This program is sponsored by National E-Government Division. Government along with other institutions and organisations like google, Reserve Bank of India educates the masses about safe handling of digital gadgets, and not to click on the link received from any unknown sources. Other initiatives of Government of India include: National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC), Appointment of Chief Information Security Officers, Personal Data Protection Bill, Cyber Swchhta Kendra and National Cyber Security Policy, 2013.
Tamil Nadu is a leader in ICT-enabled governance and a hub of IT industry. Hence, the mission of State’s IT department is “Cyber resilience Tamil Nadu”. Cyber Security Policy 2020 has been released in September to prevent cyber-attacks. High-level security governance committee for security governance has been formed to assist CERT-IN. Chief Security information officers were also appointment to curb cyber-attack.
10 steps to approach Cyber security effectively are Risk Management Regime, Secure Configuration, Network Security, Managing User Privileges, User education and awareness, Incident management, Malware prevention, Monitoring, Removable media control and Home and Mobile working. Creating awareness among the people about cyber crime and steps to safeguard themselves is mandatory.