Rural Education

India lives in her villages
– Mahatma Gandhi
Education is a basic human rights under Article 21-A of the Indian Constitution. Education is pivotal and a fundamental requirement for every citizen to improve & maximize life, gain self-confidence & knowledge and to acquire skills & attitudes.Education in India is governed and managed by the state government, union government and local (private) bodies.
Education in India are categorised into 3 types they are Formal, Informal and Non-formal. These types are categorised into different levels, such as pre-primary, primary, middle school, secondary education, higher education and vocational education. India faces several challenges in education, like dropouts, infrastructure, learning outcome, employability etc., to name a few. India follows 10+2+3, 10 years of elementary and secondary education, 2 years of higher education and 3 years of graduation, pattern of education. Types of educational institutions prevalent in India are 1) recognised institutions and 2) unrecognised institutions. There are many national level and state level educational policies framed by union and state government respectively. Indian education system has certain councils, frameworks and boards to conduct examinations, prepare books, check the quality of education, to frame rules and regulations and to give affiliation for the educational institutions in India. Geographically, Indian education can be broadly classified into rural and urban education. Let us see the rural education of our country in detail.
For a country’s development Rural Education should be given utmost importance since 66 % (according to World Bank statistics) of the total population resides in the rural areas. Government has launched many schemes like Sarva Siksha Abhiyan, Beti Bachao Beti Padhao, Samagra shiksha, Shiksha karmi project, Lok Jambish Pariyojana, eklavya model residential scheme and several other digital initiatives to combat issues like education for girl children, quality education, proper infrastructure, easy access to study materials and so on. Though the number of school going children in rural areas increases, half of the students of class v are unable to even compete with the students of class II in the schools of urban areas. The objective of rural education is to have more productive workers, increase their overall income, make them take informed decisions about farms and to innovate in agricultural affairs. Rural education does not only help in economic growth it also plays a major role in eradicating poverty and illiteracy. It also improves their standard of living. As per Unified District Information System for Education (U-DISE), 84.46% of schools, 71.72% of total student enrolment and 73.04% of teachers placed in rural areas.
Improving the percentage of literacy among the rural children and adults helps in the social development of the state. Government of Tamil Nadu has allocated funds and special projects to eradicate illiteracy in rural areas. Some of the Government initiatives are Total Literacy Movement, special literacy program for prisoners, Illam Thedi Kalvi, Karkum Bharatham, Ezhutharivu Thittam to name a few. In order to reduce and prevent school drop outs Government of TN has established Mid-day meal and breakfast scheme in addition to free books, shoes and uniform for children studying in schools run by state government. Sports, competition and culturals are always a part of urban and private school life, which has been recently implemented in Rural and government schools to motivate the children and it has been identified as a means for preventing the dropouts.
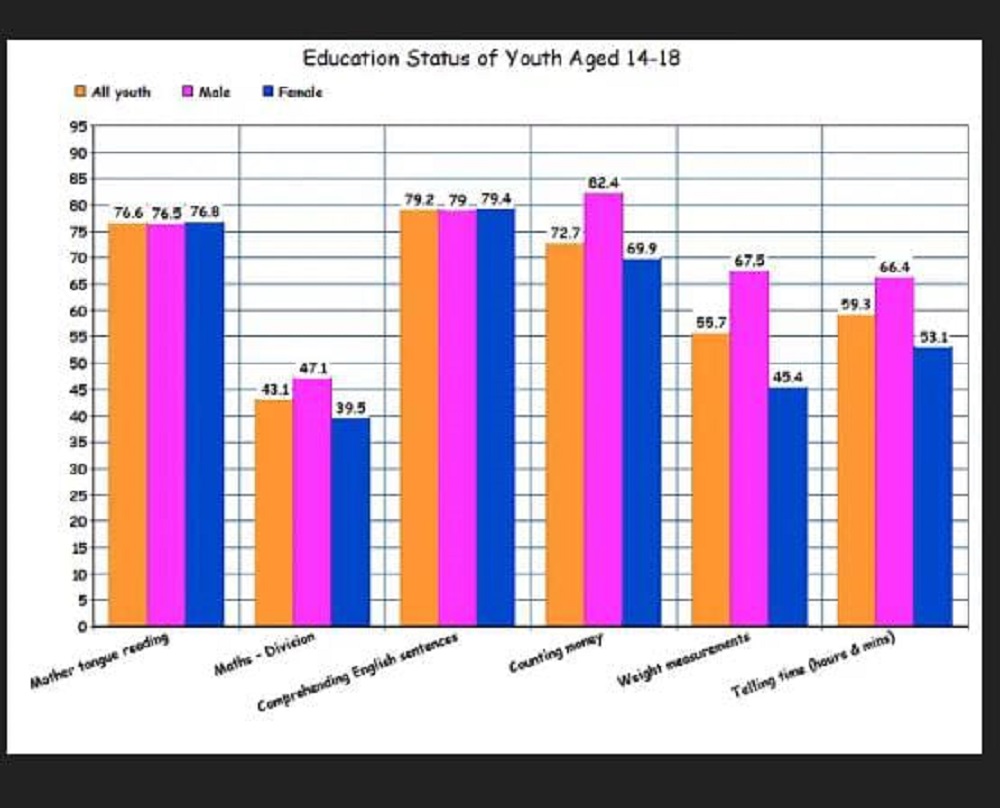
Below given is the statistics of the knowledge of students in rural areas - education status of youth aged 14-18 years old